Data Files
Control file (iocntl)
Content
The control file contains the names of the input and output files needed by the FEHM code. In addition to listing the I/O file names, the terminal (tty) output option and the user subroutine number are given. The control file provides the user an alternate means for inputting file names, terminal output option, and user subroutine number than through the terminal I/O. It is useful when long file names are used or when files are buried in several subdirectories, or for automated program execution. The elements of the file and input requirements are described in Control File or Terminal I/O Input.
Use by Program
The control file provides the FEHM application with the names of the input and output files, terminal output units, and user subroutine number to be utilized for a particular run. The default control file name is fehmn.files. If the control file is found, it is read prior to problem initialization. If not present, terminal I/O is initiated and the user is prompted for required information. A control file may use a name other than the default. This alternate control file name would be input during terminal I/O. See Control File or Terminal I/O Startup.
Auxiliary Processing
N/A
Input file (inpt)
Content
The input file contains user parameter initialization values and problem control information. The form of the file name is filen or filen.* where filen is a prefix used by the code to name auxiliary files and .* represents an arbitrary file extension. If a file name is not specified when requested during terminal I/O, the file fehmn.dat is the default. The organization of the file is described in detail in Individual Input Records or Parameters.
Use by Program
The input file provides the FEHM application with user parameter initialization values and problem control information.The input file is read during problem initialization.
Auxiliary Processing
N/A
Geometry data file (incoor)
Content
The geometry data file contains the mesh element and coordinate data. This can either be the same as the input file or a separate file.
Use by Program
The geometry data file provides the FEHM application with element and coordinate data. The geometry data file is read during problem initialization.
Auxiliary Processing
N/A
Zone data file (inzone)
Content
The zone data file contains the zone information (see macro zone). This can either be the same as the input file or a separate file.
Use by Program
The zone data file provides the FEHM application with initial geometric zone descriptions. The zone data file is read during problem initialization.
Auxiliary Processing
N/A
Optional input files
Content
The optional input files contain user parameter initialization values and problem control information. The names of optional input files are provided in the main input file to direct the code to auxiliary files to be used for data input. Their use is described in detail in Optional Input Files.
Use by Program
The optional input files provide the FEHM application with user parameter initialization values and problem control information. The optional input files are read during problem initialization.
Auxiliary Processing
N/A
Read file (iread)
Content
The read file contains the initial values of pressure, temperature, saturation, and simulation time (the restart or initial state values). It may also contain initial species concentrations for transport simulation or particle tracking data for particle tracking simulation restarts. The naming convention is similar to that for the output file. The generated name is of the form filen.ini.
Use by Program
The FEHM application uses the read file for program restarts. The read file is read during problem initialization.
Auxiliary Processing
N/A
Multiple simulations input file
Content
The multiple simulations input file contains the number of simulations to be performed and, on UNIX systems, instructions for pre- and post-processing input and output data during a multiple realization simulation. The file name is fehmn.msim.
Use by Program
The FEHM application uses the multiple simulations input file to setup control for a multiple realization simulation. It is accessed at the beginning the program.
Auxiliary Processing
N/A
Type curve data input file
Content
The type curve data input file contains parameter and data values necessary to compute dispersion delay times for the particle tracking models using type curves.
Auxiliary Processing
The FEHM application uses the type curve data input file to read the parameter and data values necessary to simulate dispersion delay times for the particle tracking models. It is accessed at the beginning the program if a particle tracking simulation using type curves is run.
Auxiliary Processing
N/A
Output file (iout)
Content
The output file contains the FEHM output. The file name is provided in the input control file or as terminal input, or may be generated by the code from the name of the input file if terminal I/O is invoked. The generated name is of the form filen.out where the “filen” prefix is common to the input file.
Use by Program
The FEHM application uses the output file for general program time step summary information. It is accessed throughout the program as the simulation steps through time.
Auxiliary Processing
This file may be accessed by scripts or user developed programs to extract summary information not recorded in other output files.
Write file (isave)
Content
The write file contains the final values of pressure, temperature, saturation, and simulation time for the run. It may also contain final species concentrations for transport simulations or particle tracking data for particle tracking simulations. This file can in turn be used as the read file in a restart run. The naming convention is similar to that for the output file. The generated name is of the form filen.fin.
Use by Program
The FEHM application uses the write file for storing state data of the simulation. It is accessed at specified times throughout the program when state data should be stored.
Auxiliary Processing
This file may be accessed by scripts or user developed programs to extract final state information not recorded in other output files.
History plot file (ishis)
Content
The history plot file contains data for history plots of variables. The naming convention is similar to that for the output file. The generated name is of the form filen.his.
Use by Program
The FEHM application uses the history plot file for storing history data for pressure, temperature, flow, and energy output. It is accessed throughout the program as the simulation steps through time.
Auxiliary Processing
This file may be used to produce history plots by external graphics programs.
Solute plot file (istrc)
Content
The solute plot file contains history data for solute concentrations at specified nodes. The naming convention is similar to that for the output file. The generated name is of the form filen.trc.
Use by Program
The FEHM application uses the solute plot file for storing history data for tracer output. It is accessed throughout the program as the simulation steps through time.
Auxiliary Processing
This file may be used to produce history plots of tracers by external graphics programs.
Contour plot file (iscon)
Content
The contour plot file contains the contour plot data. The naming convention is similar to that for the output file. The generated name is of the form filen.con.
Use by Program
The FEHM application uses the contour plot file for storing contour data for pressure, temperature, flow, energy output, and tracer output. It is accessed at specified times throughout the program when contour data should be stored.
Auxiliary Processing
This file may be used to produce contour plots by external graphics programs.
Contour plot file for dual or dpdp (iscon1)
Content
The dual or dpdp contour plot file contains the contour plot data for dual porosity or dual porosity / dual permeability problems. The naming convention is similar to that for the output file. The generated name is of the form filen.dp.
Use by Program
The FEHM application uses the dual or dpdp contour plot file for storing contour data for pressure, temperature, flow, energy output, and tracer output for dual porosity or dual porosity / dual permeability problems. It is accessed at specified times throughout the program when contour data should be stored.
Auxiliary Processing
This file may be used to produce contour plots by external graphics programs.
Stiffness matrix data file (isstor)
Content
The stiffness matrix data file contains finite element coefficients calculated by the code. It is useful for repeated calculations that use the same mesh, especially for large problems. The naming convention is similar to that for the output file. The generated name is of the form filen.stor.
Use by Program
The stiffness matrix data file is both an input and an output file the FEHM application uses for storing or reading finite element coefficients calculated by the code. The stiffness matrix data file is read during problem initialization if being used for input. It is accessed after finite element coefficients are calculated if being used for output.
Auxiliary Processing
N/A
Input check file (ischk)
Content
The input check file contains a summary of coordinate and variable information, suggestions for reducing storage, coordinates where maximum and minimum values occur, and information about input for variables set at each node. The naming convention is similar to that for the output file. The generated name is of the form filen.chk.
Use by Program
The FEHM application uses the input check file for writing a summary of the data initialization. The input check file is accessed during data initialization and when it has been completed.
Auxiliary Processing
N/A
Submodel output file (isubm)
Content
The submodel output file contains “flow” macro data that represents boundary conditions for an extracted submodel (i.e., the output will use the format of the “flow” input macro). The naming convention is similar to that for the output file. The generated name is of the form filen.subbc.
Use by Program
The FEHM application uses the submodel output file for writing extracted boundary conditions. The submodel output file is accessed during data initialization and at the end of the simulation.
Auxiliary Processing
N/A
Output error file (ierr)
Content
The output error file contains any error or warning messages issued by the code during a run. The file is always named fehmn.err and will be found in the directory from which the problem was executed.
Use by Program
The FEHM application uses the output error file for writing error or warning messages issued by the code during a run. It may be accessed at any time.
Auxiliary Processing
N/A
Multiple simulations script files
Content
The multiple simulations script files contain instructions for pre- and post-processing input and output data during a multiple realization simulation. Pre-processing instructions are always written to a file named fehmn.pre, while post-processing instructions are always written to a file named fehmn.post, and will be found in the directory from which the program was executed.
Use by Program
The FEHM application uses the multiple simulations script files for writing UNIX shell script style instructions. They are generated from information contained in the multiple simulations input file at the beginning of the program. The pre-processing instructions are then executed (invoked as a shell script) prior to data input for each realization, and the post-processing instructions are executed at the completion of each realization. The following command is used to execute the scripts:
.. code::
sh script_file $1 $2
where $1 is the current simulation number and $2 is nsim, the total number of simulations.
Auxiliary Processing
N/A
PEST output files (ispest, ispst1)
Content
The PEST output files contain output data (pressure or head, saturations, and temperatures) in a format suitable for use by the Parameter Estimation Program (PEST) (Watermark Computing, 1994). The generated names are of the form filen.pest and filen.pest1, where filen is based on the file prefix for the general output file. If an output file is not defined the default names are fehmn.pest and fehmn.pest1.
Use by Program
The FEHM application uses the PEST output files for writing parameter values generated during a run. They may be accessed at any time throughout the program as the simulation steps through time, but only values at the final state are saved.
Auxiliary Processing
The primary file (filen.pest) is generated to provide input to the Parameter Estimation Program (PEST) (Watermark Computing, 1994). The second file is generated to provide a backup of general information for review purposes.
Streamline particle tracking output files (isptr1, isptr2, isptr3)
Content
The streamline particle tracking output files contain output data from a streamline particle tracking simulation. The generated names are of the form filen.sptr1, filen.sptr2 and filen.sptr3, where filen is based on the file prefix for the tracer output file or the general output file. If those files are not defined the default names are fehmn.sptr1, fehmn.sptr2, and fehmn.sptr3.
Use by Program
The FEHM application uses the streamline particle tracking output files for writing parameter values generated during a run. They may be accessed at any time throughout the program as the simulation steps through time.
Auxiliary Processing
These files may be used to produce streamline plots or breakthrough data plots by external graphics programs.
Optional history plot files (ishis*)
Content
The optional history plot files contain data for history plots of variables. The naming convention is similar to that for the output file. The generated name is of the form filen.his, filen.trc, filen_param[.his, _his.dat, _his.csv, .trc, .dat, .csv]. “param” will depend on the output parameters selected. The extension will depend on output format selected: tecplot (.dat), comma separated variables (.csv) or default (.his, .trc).
Use by Program
The FEHM application uses the optional history plot files for storing history data for selected parameters which include: pressure, head, temperature, water content, flow, saturation, humidity, enthalpy, density, viscosity, flux, mass, displacement, stress / strain, and concentration (node based) and global output. The basic history file, filen.his, will contain run information including which parameters were selected and the output node and zone data. The basic history file, filen.trc, will contain output node data and numbers of solute species by type when concentrations are output. The parameter files are accessed throughout the program as the simulation steps through time.
Auxiliary Processing
These files may be used to produce history plots by external graphics programs.
Optional contour output files (Advanced Visual Systems [AVS], TECPLOT, and SURFER)
Content
The contour output files contain output data for the entire grid or selected zones. The content will depend on output format (avs or avsx [.avs], tecplot [.dat], or surfer [comma separated variables, .csv]) and parameters selected (material, pressure or head, saturation, temperature, flux, permeability, saturation, porosity, velocity, displacement, stress / strain, and concentration). The geometry based data can be imported into Advanced Visual Systems (AVS) UCD (unstructured cell data), TECPLOT, or SURFER graphics routines.
The contour output files each have a unique file name indicating the section type, the data type and the time step the files were created. These file names are automatically generated by the code and are of the form filen.NumberAVS_id, where filen is common to the root file name or contour output file prefix if defined, otherwise it is the input file prefix, Number is a value between 00001 and 99999, and AVS_id is a string denoting file content (see Contour File Content Tag and AVS UCD formatted FEHM output files). In general, _head are header files (only used by AVS), _geo is the geometry file, and _node the data files. The following, _mat, _sca, _vec, _con, _mat_dual, _sca_dual, _vec_dual, or _con_dual, are pre-appended to _head and _node to further identify the data selected for output. Currently all properties are node based rather than cell based.
Contour File Content Tag
| _avs_log | Log file from contour output routines |
| _geo | Geometry output file containing coordinates and cell information (AVS UCD geometry file format) |
| _grid.dat | Geometry output file containing coordinates and element connectivity (Tecplot grid file format) |
| _mat_head | AVS UCD header for material properties file. |
| _mat_dual_head | AVS UCD header for material properties file for dual or dpdp. |
| _sca_head | AVS UCD header for scalar parameter values file. |
| _sca_dual_head | AVS UCD header for scalar parameter values file for dual or dpdp. |
| _vec_head | AVS UCD header for vector parameter values. |
| _vec_dual_head | AVS UCD header for vector parameter values for dual or dpdp. |
| _con_head | AVS UCD header for solute concentration file. |
| _con_dual_head | AVS UCD header for solute concentration file for dual or dpdp. |
| _mat_node | Data output file with Material properties. |
| _mat_dual_node | Data output file with Material properties for dual or dpdp. |
| _sca_node | Data output file with Scalar parameter values (pressure, temperature, saturation). |
| _sca_dual_node | Data output file with Scalar parameter values (pressure, temperature, saturation) for dual or dpdp. |
| _vec_node | Data output file with Vector parameter values (velocity). |
| _vec_dual_node | Data output file with Vector parameter values (velocity) for dual or dpdp. |
| _con_node | Data output file with Solute concentration. |
| _con_dual_node | Data output file with Solute concentration for dual or dpdp. |
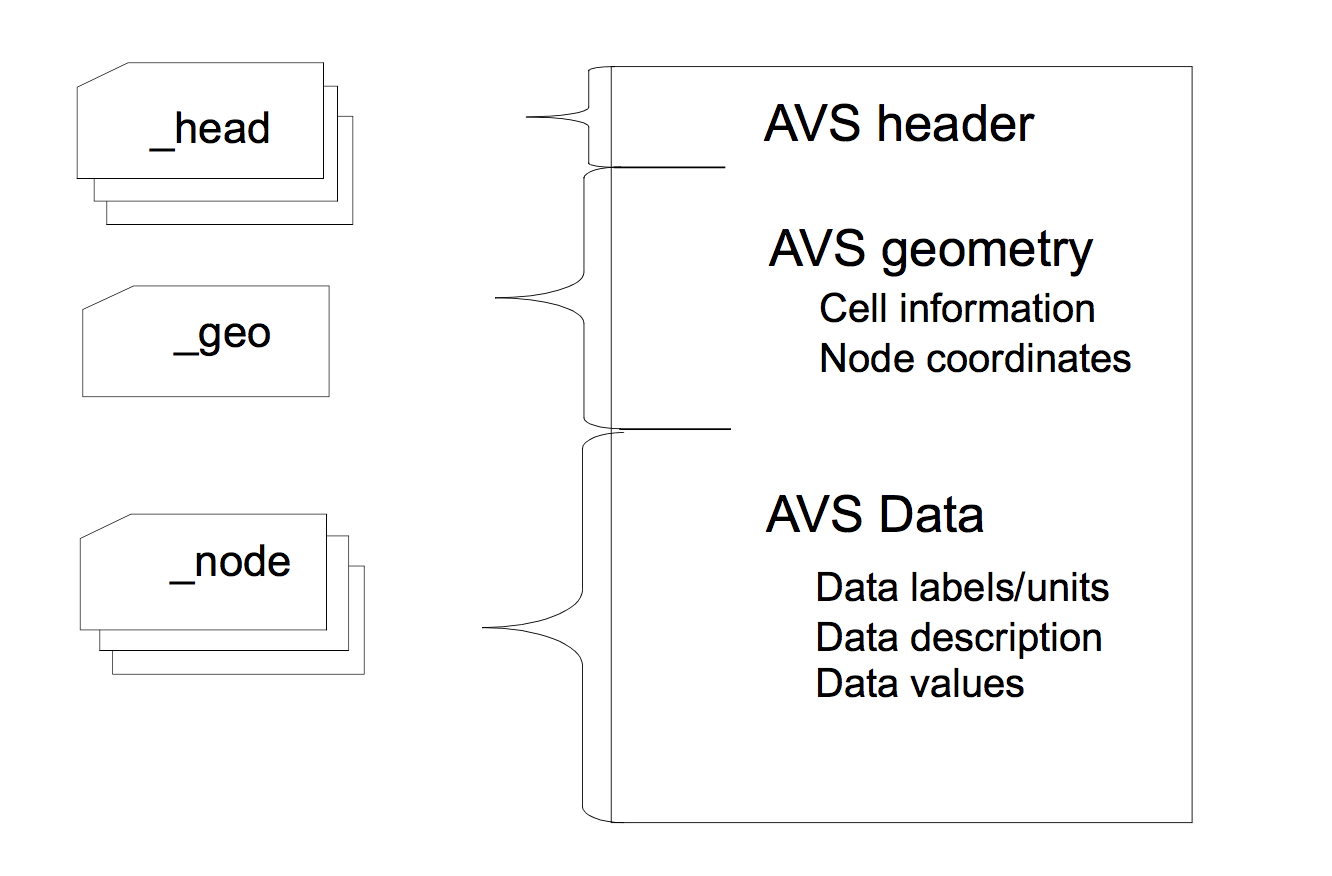 Figure 1: AVS-UCD formatted FEHM output files
Figure 1: AVS-UCD formatted FEHM output files
AVS UCD formatted FEHM output files
Use by Program
The FEHM application uses the contour output files for storing geometry based data for material properties (permeabilities and porosities), temperature, saturation, pressure, velocities, and solute concentrations in a format readable by AVS, TECPLOT or SURFER graphics. The log output file is created on the first call to the AVS write routines. It includes the code version number, date and problem title. When output for a specified time step has been completed, a line containing the file name prefix, time step, call number (the initial call is 1 and is incremented with each call to write AVS contour data) and problem time (days) is written. The header files, one for each type of data being stored, and the single geometry file are written during the first call to the AVS output routines. The node data files are written for each call to the AVS write routines, at specified times throughout the program when contour data should be stored using a specified format.
Auxiliary Processing
These files are used for visualization and analysis of data by AVS, TECPLOT or SURFER.
To use with AVS, the appropriate header file, geometry file, and data file for each node must be concatenated into one file of the form filen.inp. This can be done with the script fehm2avs for a series of files with the same root filen or manually, for example:
cat filen.10001_head filen.10001_geo filen.10001_mat_node > filen.10001.inp
Once header and geometry have been merged with data files into a single AVS file, the data can be imported into AVS using the read_ucd module.