Stratigraphic Hex Mesh Tutorial¶
Written by Guoyan Jiang (gyjiang@whu.edu.cn) with technical support from Dylan Harp (dharp@lanl.gov) and Terry Miller (tamiller@lanl.gov). The associated LaGriT tutorial is here. This example script can be downloaded here.
# -*- coding: utf-8
# This script is the PyLaGriT version of LaGriT tutorial example at
# https://lanl.github.io/LaGriT/pages/tutorial/stratigraphy/index.html.
# Written by Guoyan Jiang (gyjiang@whu.edu.cn) with technical support
# from Dylan Harp (dharp@lanl.gov) and Terry Miller (tamiller@lanl.gov).
# Import PyLaGriT class from pylagrit module
from pylagrit import PyLaGriT
import numpy
# Variables
maxX = 4000 # Max value in x direction
maxY = 4000 # Max value in y direction
maxZ = 3000 # Max value in z direction
numX = 51 # Number of points in x direction
numY = 51 # Number of points in y direction
numZ = 26 # Number of points in z direction
# Create PyLaGriT object
# This assumes that pylagritrc is being used so that lagrit_exe option does not need to be specified
lg = PyLaGriT()
#********************************************
# 01 Built HEX Mesh
#********************************************
# Create mesh object
mo = lg.create_hex()
mo.createpts_brick_xyz((numX, numY, numZ), (0,0,0), (maxX, maxY, maxZ))
# Save the mesh object
mo.dump('tmp_hex_01.inp')
# Set vertices (imt) and cells (itetlcr) to 1
mo.setatt('imt', 1)
mo.setatt('itetclr', 1)
# Set node type from connectivity of mesh
mo.resetpts_itp()
#********************************************
# 02 Use pset’s to identify (for setting boundary conditions,
# initial conditions, etc.) a set of vertices on the top
# surface of the mesh
#********************************************
# Create a pset named p_top, which contains all nodes (stride = 1 0 0)
# where the node’s Z value (zic) is greater than or equal to (ge) the top of the mesh (maxZ)
pset0 = mo.pset_attribute('zic', maxZ, 'ge', (1,0,0), 'p_top')
# Define three cylindrical objects
pset1 = mo.pset_geom((0,0,-1), (1100,360,10000), (1500,1500,0), 'rtz', (1,0,0), 'p_circle1')
pset2 = mo.pset_geom((0,0,-1), (1100,360,10000), (2500,2500,0), 'rtz', (1,0,0), 'p_circle2')
pset3 = mo.pset_geom((0,0,-1), (1100,360,10000), (2500,1500,0), 'rtz', (1,0,0), 'p_circle3')
# Intersect four psets, points belonging to the union of all given sets are preserved into the pset p_region
pset4 = mo.pset_inter([pset0, pset1, pset2, pset3], 'p_region')
# Map psets to an attribute
mo.addatt('id_top_region', vtype='vint', rank='scalar') # Creat a node-based attribute id_top_region within the mesh object
mo.setatt('id_top_region', 1) #Fill the entire attribute with 1
pset1.setatt('id_top_region', 2) #Color all nodes in the pset p_circle1 with the value 2
pset2.setatt('id_top_region', 3)
pset3.setatt('id_top_region', 4)
pset4.setatt('id_top_region', 5)
# Release the psets from memory
pset0.delete()
pset1.delete()
pset2.delete()
pset3.delete()
pset4.delete()
#********************************************
# 03 Build some surfaces to define stratigraphy.
# In a real model, the surfaces would come from some geologic framework model
# and would define geologic or hydro-geologic horizons and topography.
#********************************************
mosurf1 = lg.create_qua() # Create the top surface
p1 = (-20, -20, 1000)
p2 = (4020, -20, 1500)
p3 = (4020, 4020, 2500)
p4 = (-20, 4020, 500)
pts = [p1, p2, p3, p4]
nnodes = (numX, numY, 1)
mosurf1.quadxy(nnodes, pts)
#mosurf1.paraview()
mosurf1.minmax_xyz()
mosurf1.dump('tmp_surf1_quad.inp')
mosurf2 = lg.create_qua() # Create the bottom surface
p1 = (-20, -20, 1800)
p2 = (4020, -20, 2100)
p3 = (4020, 4020, 2800)
p4 = (-20, 4020, 800)
pts = [p1, p2, p3, p4]
nnodes = (numX, numY, 1)
mosurf2.quadxy(nnodes, pts)
#mosurf2.paraview()
mosurf2.minmax_xyz()
mosurf2.dump('tmp_surf2_quad.inp')
#********************************************
# 04 Use the surfaces to define regions and set
# vertex and cell ids
#********************************************
# Define Regions
sf1 = mosurf1.surface('sf1')
sf2 = mosurf2.surface('sf2')
r1 = mo.region('le ' + str(sf1))
r2 = mo.region('gt ' + str(sf1) + ' and ' + 'le ' + str(sf2))
r3 = mo.region('gt ' + str(sf2))
mosurf1.delete()
mosurf2.delete()
# Create Eltsets and PSets from Regions
pset1 = mo.pset_region(r1)
pset2 = mo.pset_region(r2)
pset3 = mo.pset_region(r3)
eltset1 = mo.eltset_region(r1)
eltset2 = mo.eltset_region(r2)
eltset3 = mo.eltset_region(r3)
#Set Attributes from Eltsets and PSets
pset1.setatt('imt', 1)
pset2.setatt('imt', 2)
pset3.setatt('imt', 3)
eltset1.setatt('itetclr', 1)
eltset2.setatt('itetclr', 2)
eltset3.setatt('itetclr', 3)
#********************************************
# 05 Build a fault surface and define stratigraphy
# on each side of the fault
#********************************************
# Create fault surface and surfaces to either side of fault
mosurf1_fminus = lg.create_qua()
p1 = (-20, -20, 1000)
p2 = (4020, -20, 1500)
p3 = (4020, 4020, 2500)
p4 = (-20, 4020, 500)
pts = [p1, p2, p3, p4]
nnodes = (numX, numY, 1)
mosurf1_fminus .quadxy(nnodes, pts)
#mosurf1_fminus .paraview()
mosurf1_fminus .minmax_xyz()
mosurf1_fminus .dump('tmp_s1_fm.inp')
mosurf2_fminus = lg.create_qua()
p1 = (-20, -20, 1800)
p2 = (4020, -20, 2100)
p3 = (4020, 4020, 2800)
p4 = (-20, 4020, 800)
pts = [p1, p2, p3, p4]
nnodes = (numX, numY, 1)
mosurf2_fminus.quadxy(nnodes, pts)
#mosurf2_fminus.paraview()
mosurf2_fminus.minmax_xyz()
mosurf2_fminus.dump('tmp_s2_fm.inp')
mosurf1_fplus = lg.create_qua()
p1 = (-20, -20, 1400)
p2 = (4020, -20, 1900)
p3 = (4020, 4020, 2900)
p4 = (-20, 4020, 900)
pts = [p1, p2, p3, p4]
nnodes = (numX, numY, 1)
mosurf1_fplus.quadxy(nnodes, pts)
#mosurf1_fplus.paraview()
mosurf1_fplus.minmax_xyz()
mosurf1_fplus.dump('mosurf1_fplus.inp')
mosurf2_fplus = lg.create_qua()
p1 = (-20, -20, 2200)
p2 = (4020, -20, 2500)
p3 = (4020, 4020, 3200)
p4 = (-20, 4020, 1200)
pts = [p1, p2, p3, p4]
nnodes = (numX, numY, 1)
mosurf2_fplus.quadxy(nnodes, pts)
#mosurf2_fplus.paraview()
mosurf2_fplus.minmax_xyz()
mosurf2_fplus.dump('mosurf2_fplus.inp')
mosurf_fault = lg.create_qua()
p1 = (-20, -20, -1.e4)
p2 = (4020, -20, -1.e4)
p3 = (4020, 4020, 1.e4)
p4 = (-20, 4020, 1.e4)
pts = [p1, p2, p3, p4]
nnodes = (numX, numY, 1)
mosurf_fault.quadxy(nnodes, pts)
#mosurf_fault.paraview()
mosurf_fault.minmax_xyz()
mosurf_fault.dump('mosurf_fault.inp')
# Define geometry of hydrostratigraphic model
sf1_fm = mosurf1_fminus.surface('sf1_fm')
sf2_fm = mosurf2_fminus.surface('sf2_fm')
sf1_fp = mosurf1_fplus.surface('sf1_fp')
sf2_fp = mosurf2_fplus.surface('sf2_fp')
sf_f = mosurf_fault.surface('sf_f')
r1_fm = mo.region('le ' + str(sf1_fm) + ' and ' + 'le ' + str(sf_f))
r2_fm = mo.region('gt ' + str(sf1_fm) + ' and ' + 'le ' + str(sf2_fm) + ' and ' + 'le ' + str(sf_f))
r3_fm = mo.region('gt ' + str(sf2_fm) + ' and ' + 'le ' + str(sf_f))
r1_fp = mo.region('le ' + str(sf1_fp) + ' and ' + 'gt ' + str(sf_f))
r2_fp = mo.region('gt ' + str(sf1_fp) + ' and ' + 'le ' + str(sf2_fp) + ' and ' + 'gt ' + str(sf_f))
r3_fp = mo.region('gt ' + str(sf2_fp) + ' and ' + 'gt ' + str(sf_f))
mosurf1_fminus.delete()
mosurf2_fminus.delete()
mosurf1_fplus.delete()
mosurf2_fplus.delete()
mosurf_fault.delete()
# Set fault node and element materials
pset1_fm = mo.pset_region(r1_fm)
pset2_fm = mo.pset_region(r2_fm)
pset3_fm = mo.pset_region(r3_fm)
pset1_fp = mo.pset_region(r1_fp)
pset2_fp = mo.pset_region(r2_fp)
pset3_fp = mo.pset_region(r3_fp)
eltset1_fm = mo.eltset_region(r1_fm)
eltset2_fm = mo.eltset_region(r2_fm)
eltset3_fm = mo.eltset_region(r3_fm)
eltset1_fp = mo.eltset_region(r1_fp)
eltset2_fp = mo.eltset_region(r2_fp)
eltset3_fp = mo.eltset_region(r3_fp)
#Set Attributes from Eltsets and PSets
mo.setatt('imt', 7)
mo.setatt('itetclr', 7)
pset1_fm.setatt('imt', 1)
pset2_fm.setatt('imt', 2)
pset3_fm.setatt('imt', 3)
pset1_fp.setatt('imt', 4)
pset2_fp.setatt('imt', 5)
pset3_fp.setatt('imt', 6)
eltset1_fm.setatt('itetclr', 1)
eltset2_fm.setatt('itetclr', 2)
eltset3_fm.setatt('itetclr', 3)
eltset1_fp.setatt('itetclr', 4)
eltset2_fp.setatt('itetclr', 5)
eltset3_fp.setatt('itetclr', 6)
#********************************************
# 06 Define a polyline and truncate the exterior boundary of the mesh with the polyline
#********************************************
# Read boundary polygon file
mobndry = lg.read('basin_bnd_ply_rescale.inp')
# Extrude the polyline into a vertical surface
mofence = mobndry.extrude(3200, 'const', 'volume', [0, 0, -1])
mobndry.minmax_xyz()
mofence.minmax_xyz()
# Translate the extrusion to make it cover the vertical extent of the hex mesh
mofence.trans((0, 0, -3100), (0, 0 ,0))
mofence.minmax_xyz()
#mofence.paraview()
#mofence.dump('3D_vertical_surface.inp')
#mo.dump('cube.inp')
# Truncate mesh
sf_bndry = mofence.surface('sf_bndry')
r_bndry = mo.region('ge ' + str(sf_bndry))
pset_bndry = mo.pset_region(r_bndry)
mobndry.delete()
mofence.delete()
# Method 1: Only remove a cell if ALL vertices are outside
e_delete1 = pset_bndry.eltset('exclusive')
# Method 2: Remove a cell if the centroid (average of all vertices) is outside
e_delete2 = mo.eltset_region(r_bndry)
# Method 3: Remove a cell if one or more vertices are outside
e_delete3 = pset_bndry.eltset('inclusive')
#mo.addatt('id_in_out_bndry', vtype='vint', rank='scalar', length='nelements')
mo.add_element_attribute('id_in_out_bndry', vtype='vint')
mo.setatt('id_in_out_bndry', 4) #Fill the entire attribute with 4
e_delete3.setatt('id_in_out_bndry', 3)
e_delete2.setatt('id_in_out_bndry', 2)
e_delete1.setatt('id_in_out_bndry', 1)
eltset4 = mo.eltset_attribute('id_in_out_bndry', 4, 'eq')
eltset3 = mo.eltset_attribute('id_in_out_bndry', 3, 'eq')
#eltset2 = mo.eltset_attribute('id_in_out_bndry', 2, 'eq')
#eltset1 = mo.eltset_attribute('id_in_out_bndry', 1, 'eq')
mo.rmpoint_eltset(eltset4, False, False)
mo.rmpoint_eltset(eltset3, True, True)
#********************************************
# 07 Refine the mesh around the fault
#********************************************
f_zone = mo.intersect_elements(sf_f, 'f_zone')
fz_i = mo.eltset_attribute('f_zone', 0, 'gt') #Non-zero indicates intersection
fz_i.refine()
mo.delatt('f_zone')
mo.status (brief=True)
#sf_f.delete()
#sf1_fm.delete()
#sf2_fm.delete()
#sf1_fp.delete()
#sf1_fp.delete()
#sf_bndry.delete()
#********************************************
# 08 Insert a couple of 'wells' by refining the mesh and identifying a line of nodes
# that will be the well source/sink for boundary conditions.
#********************************************
Well1X = 1234.56
Well1Y = 1987.65
Well2X = 2243.21
Well2Y = 1212.34
Radius = 25
NRadius = 2
#Well 1
mowell1 = lg.create_tet()
mowell1.createpts_rtz((NRadius, 9, numZ), (0, 0, 3100), (Radius, 360, 1500)) #Create a cylindrical point cloud
mowell1.filter() # Filter (delete) points that are too close ( default distance <=1.e-16) or duplicate points
mowell1.rmpoint_compress() # Remove all marked nodes and correct the itet array
mowell1.setatt('imt', 1)
mowell1.connect() # Connect the point cloud
mowell1.resetpts_itp()
mowell1.minmax_xyz()
mowell1.trans((0, 0, 0), (Well1X, Well1Y, 0))
mowell1.minmax_xyz()
#mowell1.paraview()
mowell1.dump('tmp_well1.inp')
#Well 2
mowell2 = lg.create_tet()
mowell2.createpts_rtz((NRadius, 9, numZ), (0, 0, 3100), (Radius, 360, 2200))
mowell2.filter()
mowell2.rmpoint_compress()
mowell2.setatt('imt', 1)
mowell2.connect()
mowell2.resetpts_itp()
mowell2.minmax_xyz()
mowell2.trans((0, 0, 0), (Well2X, Well2Y, 0))
mowell2.minmax_xyz()
#mowell2.paraview()
mowell2.dump('tmp_well2.inp')
# Join the two distinct wells into a single mesh object
mowells = lg.merge([mowell1, mowell2])
mowells.dump('tmp_wells.inp')
#mowells.paraview()
# Refine the mo around the wells
# First pass refinement
w_zone = mo.intersect_elements(mowells, 'w_zone')
wz_i = mo.eltset_attribute('w_zone', 0, 'gt') #Non-zero indicates intersection
wz_i.refine()
mo.setatt('w_zone', 0)
#wz_i.delete()
# Second pass refinement
w_zone = mo.intersect_elements(mowells, 'w_zone')
wz_i = mo.eltset_attribute('w_zone', 0, 'gt') #Non-zero indicates intersection
wz_i.refine()
mo.setatt('w_zone', 0)
#wz_i.delete()
mohex = mo.grid2grid_tree_to_fe() #Quadtree or octree grid to grid
#mo.status (brief=True)
# Identify the column of vertices closest to the well center.
#Well1
mo_pts1 = lg.create()
mo_pts1.createpts_rtz((2, 2, 1000), (0, 0, 3100), (Radius, 360, 2200))
mo_pts1.trans((0, 0, 0), (Well1X, Well1Y, 0))
#Well2
mo_pts2 = lg.create()
mo_pts2.createpts_rtz((2, 2, 1000), (0, 0, 3100), (Radius, 360, 2200))
mo_pts2.trans((0, 0, 0), (Well2X, Well2Y, 0))
mo_pts = lg.merge([mo_pts1, mo_pts2])
mo_pts.filter()
mo_pts.rmpoint_compress()
# Compute a distance field attribute
mo.compute_distance(mo_pts, option='distance_field', attname='dfield_well')
mo_pts1.delete()
mo_pts2.delete()
mo_pts.delete()
mowell1.delete()
mowell2.delete()
mowells.delete()
# Describe all nodes within 32, 16, 8, 4, 2 and 1 meters of the wells.
pwell = mo.pset_attribute('dfield_well', 1.0, 'le', (1,0,0), 'pwell1')
pwell.dump('zone_radius_01.0.zone')
pwell = mo.pset_attribute('dfield_well', 2.0, 'le', (1,0,0), 'pwell2')
pwell.dump('zone_radius_02.0.zone')
pwell = mo.pset_attribute('dfield_well', 4.0, 'le', (1,0,0), 'pwell4')
pwell.dump('zone_radius_04.0.zone')
pwell = mo.pset_attribute('dfield_well', 8.0, 'le', (1,0,0), 'pwell8')
pwell.dump('zone_radius_08.0.zone')
pwell = mo.pset_attribute('dfield_well', 16.0, 'le', (1,0,0), 'pwell16')
pwell.dump('zone_radius_16.0.zone')
pwell = mo.pset_attribute('dfield_well', 32.0, 'le', (1,0,0), 'pwell32')
pwell.dump('zone_radius_32.0.zone')
mo.dump('Hex_mesh.inp')
#********************************************
# 09 Convert hex mesh to tet mesh
#********************************************
motet = mohex.copypts()
motet.setatt('imt', 1)
motet.setatt('itp', 0)
motet.connect(option1='check_interface')
motet.resetpts_itp()
motet.interpolate_voronoi('imt', mohex, 'imt')
motet.interpolate_map('itetclr', mohex, 'itetclr')
#Remove all nodes and elements with imt and itetclr values of 7
motet.rmmat(7)
#pset7 = motet.pset_attribute('imt', 7, 'eq', (1,0,0), 'pset7')
#motet.rmpoint_pset(pset7)
#eltset7 = motet.eltset_attribute('itetclr', 7, 'eq')
#motet.rmpoint_eltset(eltset7, True, True)
motet.rmpoint_compress()
motet.resetpts_itp()
# Visualize connected mesh using ParaView
# This assumes that pylagritrc is being used so that exe option does not need to be specified
#motet.paraview()
motet.dump('Tet_mesh.inp')
#********************************************
# 10 Write tet mesh files for FEHM
# FEHM uses node based materials and properties
#********************************************
#motet.resetpts_parent()
motet.filter()
motet.rmpoint_compress()
motet.resetpts_itp()
motet.minmax('imt')
motet.setatt('itetclr', 1)
#motet. tri_mesh_output_prep()
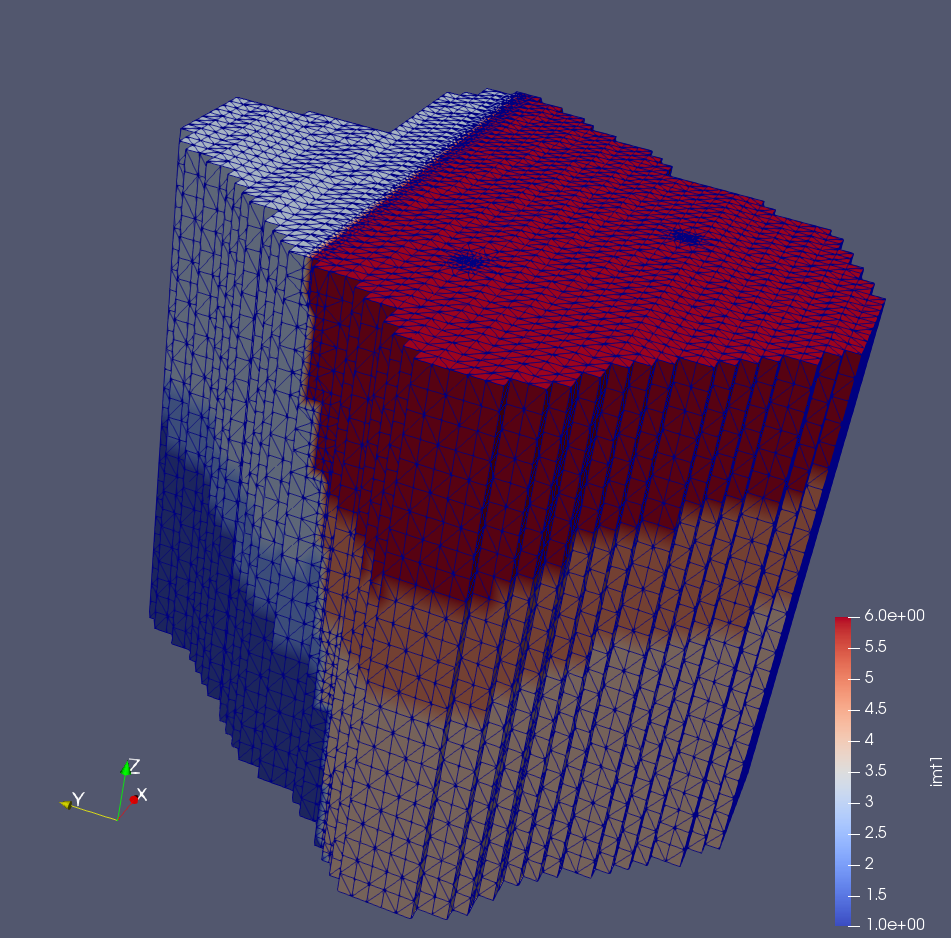
motet.dump_fehm('Example3')
The final result: