REFINE
The refine command is used to create more elements. The method in which these new elements are formed is based on the refine_method
chosen. The refine criteria used in these methods are defined at Grid Refinement Section.
SYNTAX
refine/refine_method/ [field]/ [interpolation]/refine_type /ifirst,ilast,istride/xvalue/xvalue2/xvalue3/inclusive_flag/ refine/roughness ///edge/ifirst,ilast,istride/distance/surface_name/exclusive or inclusive refine/edge_list ///edge/ end_points refine/interface /// edge/pset,get,psetname refine / eltset or element_set / eltset,get,esetname
Refine Methods
junction will refine object where field crosses xvalue
constant will refine object where field > xvalue
delta will refine object where delta(field) > xvalue
lambda will refine object where lambda(field) < xvalue
maxsize will refine object where object > xvalue. Size refers to volume for tets, area for face, and length for edges.
aspect will refine where aspect ratio < xvalue
addpts will refine explicitly by adding a set of nodes defined in pset,get,psetsname
rivara edges longer than xvalue will be refined according to the principle that a refined edge candidate is the longest edge in
any element that contains it. This results in a recursive refinement procedure that adds neighboring edges to the refinement
candidate list until no neighbor edge is longer then the candidate. refine_type must be edge. Arguments field and
interpolation are ignored. This method of refinement, when used with a pset, produces a nicely graded mesh.
rivara_boundary applies the rivara algorithm, but will only bisect edges on external boundaries.
rivera_truncated applies the rivara algorithm, but restricts the neighborhood search to the edges in the selected pset. If the
pset is the entire mesh, this method has the same behavior as rivara.
roughness will refine based on the distance of the endpoint of an edge to the plane determined by the synthetic normal with
respect to a specified surface at the other endpoint of the edge. This is intended to increase refinement on surfaces near corners
or around sharp bends in surfaces. xvalue is the distance, the surface_name must follow the xvalue distance argument.
edge_list will bisect a set of edges specified by the node numbers of the endpoints of the edges. refine_type must be
edge followed by a list of end_points making up the edge_list.
element_set or eltset will refine all elements in a specified element set. The mesh object may be tri, quad, tet or
hex. Internally a node set will be created from the chosen elements. Because of the conversion from element set to point
set, it is possible that some element not in the original element set will have all of its nodes as members of the internally
constructed points set and hence will be refined. The default refine_method is constant; refine_type is element;
inclusion_flag is exclusive. Their are no other arguments after the element set name.
interface will bisect a set of non-interface edges of tets all of whose vertices are interface nodes. Valid only for 3D
tetrahedral grids and is useful to ‘unlock’ tetrahedra that are stuck because all of their vertices lie on interface surfaces.
After the refine operation these tetrahedral will be replaced by tetrahedra containing a vertex that is not on the surface - thus
allowing later smooth or massage operations more freedom to improve the grid.
The following are unavailable or untested:
spawn spawns new nodes at the locations given. It finds the existing edge that is closest to the
desired node It then refines that edge and moves the resulting node to the desired location provided that the move does not invert any elements.
cel calls CEL (create on edge length). Takes a mesh object and bisects edges that
(i) have both endpoints in the list of selected mass points, and (ii) have length greater than TOLLENGTH.
The process is recursive in that new nodes are added to the list of mass points, meaning that newly created edges can
be refined until all the edges in the mesh have length less than TOLLENGTH.
This leads to recursive refinement with nondegrading element aspect ratios.
minsize, lambdade, and rmelements are no longer supported.
Refine Type
refine_type specifies what object will be refined and how that object will be refined:
- element or tet in 3D will refine elements by placing a point in the center of the element.
- element in 2D (triangle) will refine element by refining all edges of the triangle.
- face in 3D will refine facets by placing a point in the center of the facet.
- face in 2D (triangle) will refine face by refining all edges of the face.
- edge will refine edges by placing a point on the midpoint of the edge.
- faceedge will refine facets by refining all edges of the facet.
- tetedge will refine elements by refining all edges of the element.
Refine Options
field must refer to a previously defined attribute of the current Mesh Object.
interpolation specifies how to interpolate the field to give field
values to the new nodes created. The valid types are linear, log, and sinh.
range is the selection of points designated by node numbers for ifirst,ilast,istride or pset,get,pname. 1,0,0 will select all
nodes in the Mesh object.
xvalue [/xvalue2/xvalue3/] is the real number usually indicating a size for the different refine methods. Most of the refine methods do not
use the second and third values so their argument positions will be empty ///.
inclusion_flag is an optional flag specifing if refinement is an inclusive or an exclusive operation. By default, all operations are
exclusive. For inclusive, if an edge refinement is specified restricted to a pset, then an edge is eligible for refinement if either
or both of the end points belong to the pset selected. If the inclusion_flag is exclusive then both end points must be in the
pset. The implemented values are inclusive and exclusive.
QUADTREE and OCTREE REFINEMENT
Quad and hexahedral elements may be refined creating quad tree and octree meshes. Three new Mesh object attributes are added during this
operation. The refine_type must be element. The refine_method must be constant, junction or maxsize.
The values for /xvalue/xvalue2/xvalue3/ should be /-1.,0.,0./. For an element set, use
the shortened syntax refine/element_set/eltset,get,esetname.
The element attributes added to the Mesh object are:
itetlev is an integer attribute with the level of refinement. An unrefined mesh element has itetlev(ie)=0, one level of refinement itetlev(ie)=1, etc.
itetkid is a pointer to a child element number. If nothing has been done to change element numbering, it is element number of the first child element created and the rest of the children are in sequence after the first child. If itetkid(ie)=0 , the element has not been refined further.
itetpar is a pointer to the parent element at refinement level. itetlev(ie)-1.
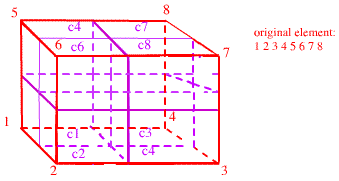
Quad meshes will have 4 children for each refined element. Hex meshes will have 8 children. The children are generated sequentially; The first child will contain the first local node of the parent element, the other elements are created in the order shown in this diagram.
For example in the picture below, element e1 is refined to create 8 children, c1, c2, c3, c4, c5, c6, c7, c8.
The table gives the octree attribute values for each of the elements.
| Element # | itetlev | itetkid | itetpar | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| c1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| c1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| c2 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| c3 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| c4 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| c5 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| c6 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| c7 | 8 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| c8 | 9 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
One can control refinement so that a hex is broken into either 8, 4 or 2 elements and a quad is broken into either 4 or 2 elements. This is
controlled with the principal refine direction choice prd_choice parameter. This syntax works assuming imt values are greater or equal
to zero with principal refine direction chosen through a combination of “123” prd_choice indicators as defined below. The command line
used is:
refine/constant/itetclr/linear/element/1,0,0/-1.,0.,0./exclusive/amr prd_choice
or with element selection (based on pset and inclusive/exclusive options):
refine/constant/imt1/linear/element/pset,get,pname/-1.,0.,0./inclusive/ amr prd_choice
The parameter prd_choice indicates the chosen principal refinement direction based on the local hex element topology as defined by edge numbers,
for instance, quad edge 1 is in the x direction relative to the local topology.
- 1 refine along x direction, 1 hex->2 hex, 1 quad->2 quad (quad edges 1 and 4)
- 2 refine along y direction, 1 hex->2 hex, 1 quad->2 quad (quad edges 2 and 3)
- 3 refine along z direction, 1 hex->2 hex, 1 quad->4 quad
- 12 refine along x and y direction, 1 hex->4 hex, 1 quad->4 quad
- 13 refine along x and z direction, 1 hex->4 hex, 1 quad->4 quad
- 23 refine along y and z direction, 1 hex->4 hex, 1 quad->4 quad
- 123 refine xyz with prd amr routines, 1 hex->8 hex, 1 quad->4 quad
- 0 refine xyz with default amr refinement, 1 hex->8 hex, 1 quad->4 quad
EXAMPLES
pset / prefine / union / prefine1 prefine2 prefine3
eltset / erefine / inclusive / pset get prefine
refine/ eltset / eltset,get,erefine
will octree refine hex elements belonging to the set of points named prefine
refine / maxsize ///edge /pset,get,something / .25
will refine element where edge is longer than .25
refine/constant/concentration/log /edge/1,0,0/25.0 /// inclusive
will refine where concentration is greater than 25.
refine /addpts///tet /pset,get,newpoints/
refine explicitly by adding the new nodes defined in the set newpoints
refine /rivara///edge/pset,get,p1/.5///inclusive
refine all edges containing at least one node in pset p1 that are longer than .5. Using the ‘rivera’ algorithm may result in edges not containing nodes in the pset to be refined.
refine/rivara_truncated///edge/pset,get,p1/.5///exclusive
rivera_truncated, exclusive will refine only edges both of whose endpoints are in the selected pset named p1
refine/rivara_boundary///edge/1,0,0/.25
rivara_boundary will only refine boundary edges.
refine/roughness///edge/1,0,0/.28/ptop/inclusive
will refine based on .28 distance to the surface named ptop.
refine/edge_list///edge/1 2 23 47
will refine the edge with end points 1 and 2 AND the edge with end points 23 and 47.
eltset / elem3 / id_elem1 / eq / 3
refine/eltset / eltset,get, elem3
will create a node set from the element set named elem3 and refine using the constant option.
refine/constant/imt1/linear/element/pset,get,pbox/-1.,0.,0./inclusive
create a quadtree refined quad mesh
eltset / elm2 / itetclr / eq / 2
pset/ pelm2 / eltset elm2
refine/constant/imt1/linear/element/pset,get,pelm2/-1.,0.,0./inclusive/amr 12
refine the material 2 elements of a hex mesh , do not refine in the Z vertical direction
refine/constant/imt1/linear/element/pset,get,pelm2/-1.,0.,0./inclusive/amr 3
refine the material 2 elements of a hex mesh , refine only in the Z vertical direction
Octree Example with loop
Use a loop to refine up to itetlev = 3 but not 4. This will select elements with itetlev < 3 to refine.
* Refine to octree itetlev= 3 elements that are intersected by cmo_3
*
define / CMO_OBJ / cmo_3
define / LEVEL / 3
define / LOOP_MAX / 4
*
loop / do / LOOP_VAR 1 LOOP_MAX 1 / loop_end infile refine_object.mlgi
The loop uses this infile refine_object.mlgi
**************************************** * * Refine based on intersection with object * **************************************** * External definitions * * CMO_HEX - Mesh object to be intersected * CMO_OBJ - Mesh object that intersects CMO_HEX * LEVEL - refine level 0, 1, 2, 3, ... * **************************************** * cmo / printatt / CMO_HEX / -xyz- / minmax cmo / printatt / CMO_OBJ / -xyz- / minmax * * * Refine elements that are intersected by CMO_OBJ * cmo / setatt / CMO_HEX / xsect / 1 0 0 / 0 intersect_elements / CMO_HEX / CMO_OBJ / xsect cmo / select / CMO_HEX eltset / e_obj / xsect / gt / 0 * * Add this just in case. If it already exists, nothing * will happen. If it does not exist, it gets added and set to zero * cmo/addatt/CMO_HEX/itetlev/vint/scalar/nelements * eltset / elev / itetlev / le / LEVEL eltset / e_refine / inter / elev e_obj * refine/eltset / eltset,get, e_refine rmpoint / compress eltset / e_obj / delete eltset / e_refine / delete **************************************** cmo / select / CMO_HEX cmo / printatt / CMO_HEX / itetlev / minmax * finish