UPSCALE
The upscale command is used to interpolate attribute values from nodes of a fine source mesh to node attributes of a coarse sink mesh. This is most often used to assign geostatistical property values from an application to the computational mesh for modeling.
This command finds dense source nodes that are within the Voronoi cell of every node in the coarser sink mesh. The voronoi volume around each sink node is the bucket that captures all node values to compute. Nodes on the voronoi boundaries are assigned to two or more sink nodes. Then the attributes of all the source nodes within a source node’s cell are upscaled into a single value based on the chosen method.
A kdtree node search is used to find the source mesh nodes located in each of the Voronoi sink point volumes. It is possible for source nodes to occur on the boundary of multiple Voronoi volumes. By default, all nodes found in each Voronoi volume are used to upscale to the enclosed sink node. In this case, source nodes on multiple Voronoi boundaries will be included in upscale calculations more than once.
It is important that the source points be denser than the sink mesh node spacing. If no source points are found within a voronoi volume, the source point is given a value of 0.
Geostat data sometimes generate very small values close to zero that are not appropriate for modeling. It is recommended that a mininum reasonable value be assigned. Be sure the range of source values are what is intended.
For the averaging methods, make sure there are no source values of 0.
SYNTAX
upscale / scale_method / cmosink, attsink / range / cmosrc, attsrc / &
[boundary_choice] [keepatt] [set_id]
Required:
scale_method is the choice of upscale calculation applied to each
set of source nodes within each sink Voronoi cell where x(1) to x(n)
are the values of source nodes 1 to n found for the sink point.
The following are valid scale methods:
-
ariave For each sink point, calculate the arithmetic mean of n values from source attribute attsrc
sink_val = (x(1) + x(i)… + x(n)) / n example: for 4 values; 1,2,3,4 ariave = 2.5 -
geoave For each sink point, calculate the geometric average of n values found in attsrc
sink_val = ( x(1) * x(i)… * x(n) ) * *(1/n) example: for 4 values; 1,2,3,4 geoave = 2.21336 -
harave For each sink point, calculate the harmonic mean of n values from source attribute attsrc
sink_val = n / ( 1/x(1) + 1/x(i)… + 1/x(n) ) example: for 4 values; 1,2,3,4 harave = 1.92 -
min or max For each sink point, assign the min or max source attribute from n values found in attsrc
sink_val = min(x(1),x(i),x(n)) example: for 4 values; 1,2,3,4 min = 1
sink_val = max(x(1),x(i),x(n)) example: for 4 values; 1,2,3,4 max = 4 -
sum For each sink point, calculate the sum of n values from source attribute attsrc
sink_val = x(1) + x(i)… + x(n) example: for 4 values; 1,2,3,4 sum = 10
cmosink, attsink are the cmo name and attribute name to write sink values into. The scale method detirmines which calculation is
applied to the source attribute value and written to the sink attribute. All integer attributes are converted to double for the
calculations. The resulting values are then converted to the nearest integer if the sink attribute is integer.
range is the set of sink nodes to write scaled values to. 1,0,0 will select all sink nodes
cmosrc, attsrc are the cmo name and attribute name are the cmo and attribute to interpolate from. Points from the source grid will be
located within the Voronoi volumes of sink nodes.
Boundary options
Optional parameters appearing after the source cmo attribute name are optional and may appear in any order.
boundary_choice provides a method of choice when source nodes are
found on the boundary of multiple Voronoi volumes of sink nodes. By
default, each set of souce nodes found within each volume are used
to calculate an upscale value for the sink node. In this case if
duplicate nodes occur on multiple cells, the sum number of nodes
used in upscale calculations will exceed the sum total of nodes in
the source mesh. If the number of source nodes used must equal the
number of source mesh nodes, choose an boundary_choice to detirmine
which sink volume an boundary node should be assigned to. The result
is a one-to-one correspondence with each source point assigned to a
single sink node id which is stored in source attribute pt_gtg.
Source nodes that are found on shared Voronoi boundaries are flagged
in source attribute dups_gtg.
-
single selects the Voronoi volume of the first sink node encountered and does not use any after that. This method can be used for situations that require the sum of nodes in each Voronoi space to equal the total of source points used. This one-to-one correspondence is written to the source cmo attribute pt_gtg. This attribute can be reused during multiple calls to the upscale command and will greatly reduce CPU time.
-
divide not implemented.
-
multiple uses all source nodes found in each sink Voronoi volume.
Added Attribute options
The following options are used with multiple calls to upscale with the same two grids. It keeps source attributes created during the search routines and uses these attributes to look up associated node numbers.
The upscale command uses kdtree to create the source attribute pt_gtg that associates source nodes to sink node volumes. Note that this correlation is one-to-one and source nodes sharing multiple Voronoi volume boundary are tagged in a second source attribute called dups_gtg.
-
delatt deletes any attributes created during the kdtree searches. By default these attributes are removed.
-
keepatt keeps attributes pt_gtg and dups_gtg created during the kdtree searches. The source node attribute pt_gtg has the first found sink node id. The node attribute dups_gtg is flagged each time the source node occurs in a sink Voronoi cell, allowing the user to find source nodes on cell boundaries. Use of this attribute will greatly reduce CPU time.
-
set_id creates and keeps the source attribute pt_gtg containing sink id numbers found from the sink mesh. This is the same attribute created and kept for the keepatt option except that if the attribute already exists, it is deleted and re-created with a new search. This is recomended if the pt_gtg attribute exists, but user is not sure the current sink mesh is the same as used to create the attribute.
EXAMPLES
upscale / sum / cmo_sink icount /1,0,0/ cmo_src ival
upscale / sum / cmo_sink icount /1,0,0/ cmo_src ival/ single keepatt
upscale / min / cmo_sink imin /1,0,0/ cmo_src ival/ single keepatt set_id
upscale / max / cmo_sink imax /1,0,0/ cmo_src ival/ keepatt
upscale / ariave / cmo_sink ave_val /1,0,0/ cmo_src xval/
upscale / harave / cmo_sink har_val /1,0,0/ cmo_src xval/
upscale / geoave / cmo_sink geo_val /1,0,0/ cmo_src xval/
upscale / sum / cmo_sink icount /1,0,0/ cmo_src ival
In this example, search will find the sets of source nodes enclosed within each sink Voronoi cell.The ival attribute values are added for each set and written to the sink icount attribute. Because the attribte ival has all values set to 1, the icount attribute will contain the number of source nodes found in each Voronoi volume. The source node values will be counted regardless if they are on a Voronoi boundary and are in multiple Voronoi volumes. The result with duplicate boundary points will be a sum of points used greater than the total number of source mesh points.
upscale / sum / cmo_sink icount /1,0,0/ cmo_src ival/ single keepatt
This is the same as above except that duplicate boundary points will be counted for the first found Voronoi volume and skipped thereafter. This one-to-one correspondance of source nodes to sink Voronoi volume will be stored in the source attributes pt_gtg with sink node numbers, and dups_gtg containing flags of the duplicate boundary points. These attributes will not be deleted.
These images show the 10 numbered sink points and the 1221 source points. In this example all source points have an imt1 value of 1. The sink points each have a value in icount equal to the number of nodes used for the associated Voronoi volume. The red lines show the Voronoi cell boundaries for the 10 sink points.
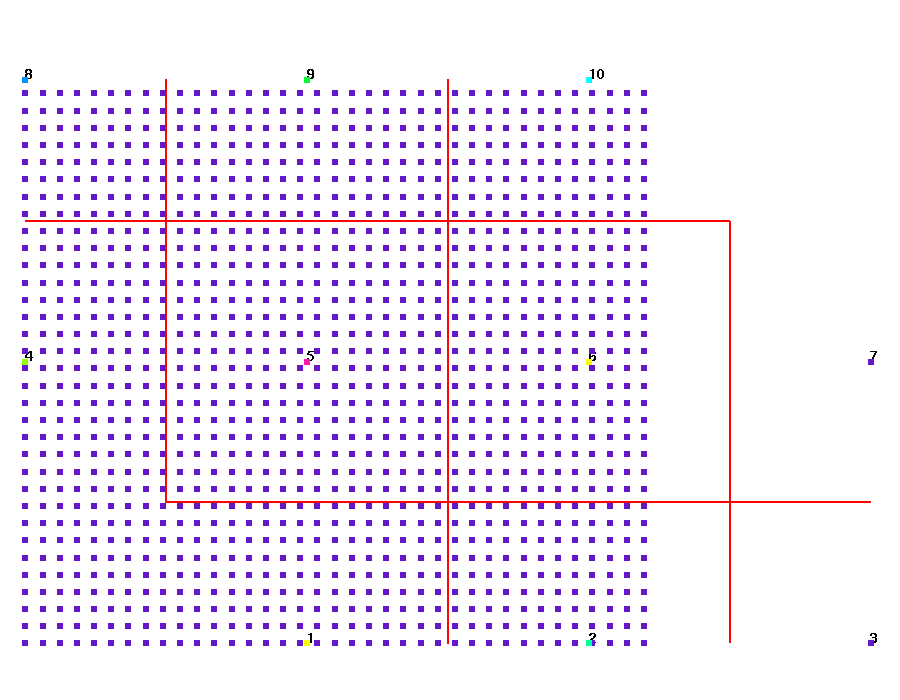
Source points all equal to 1, Sink points colored by upscaled value.
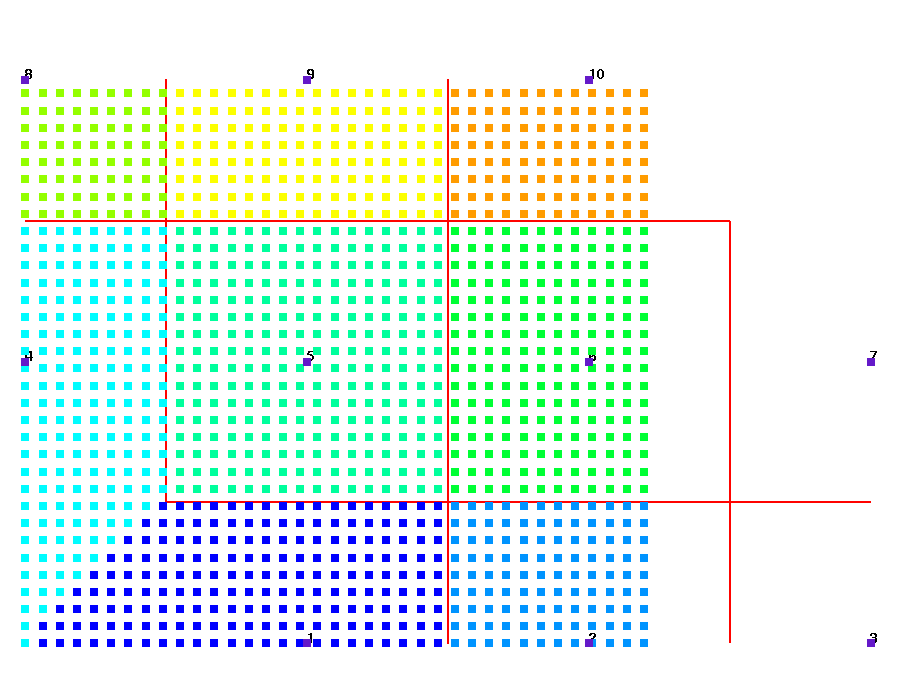
Source points colored by associated sink node id, attribute pt_gtg.
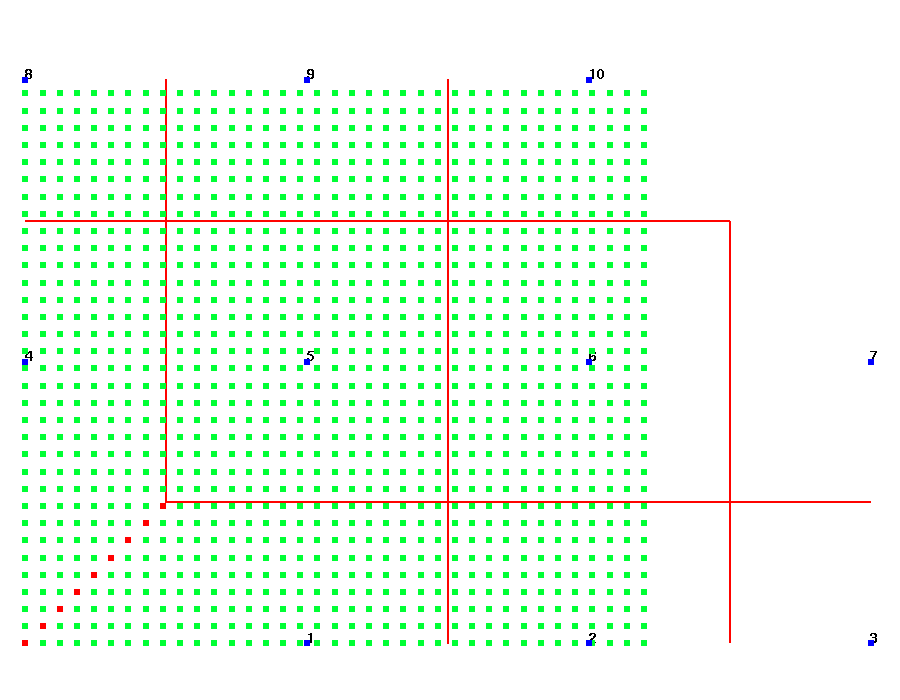
Source points colored by number of duplicates cell boundaries, attribute dups_gtg.