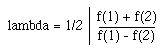I. Edges
Each edge is tested separately to see if it should be tagged for refinement or derefinement.
Definition:
c = a user supplied tolerance
f(i) = value of the field variable f at node i
L = length of the edge
For the edge between nodes 1 and 2, we have
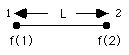
Criteria:
1) Junction: Refine if the edge field values straddle c.
Tag for refinement if f(1) > c and f(2) < c or f(1) < c and f(2) > c
example: For c = 0, refine if f changes sign across the edge.
2) Constant: Refine if the edgeís field values exceed c.
Tag for refinement if f(1) > c or f(2) > c
3) Maxsize: Refine if the edge length exceeds c.
Tag if l > c
4) Delta: Refine if the magnitude of the difference of the field values at the edge ends exceeds c.
Tag if f(1) - f(2) > c
5) Lambda Refine: Refine if lambda/dx < c. Where dx is a scale length (here taken to be the edge length).
Generally lambda/dx is a quality measure of the discretization. A larger value of usually indicates a better grid discretization. There are some special cases. If one of the field values is zero as could happen on a boundary, then lambda/dx 1/2. If f(1) is equal to f(2) then lambda/dx is divergent but the algorithm uses a small number e = .000001 added to the denominator lambda/dx to give a large but finite value of lambda/dx thus indicating a good discretization.