SimFrac object - all functions¶
Complete list of functions on the SimFrac Class
- class pysimfrac.src.general.SimFrac(lx=None, ly=None, h=None, nx=None, ny=None, shear=None, method=None, units=None, pickle_file=None)[source]
The SimFrac Object
- Parameters:
self (simFrac Object) –
units (string) – SI units for domain size, e.g., mm
lx (float) – Length of domain in x direction
ly (float) – Length of domain in x direction
h (float) – Dicretization length of domain. Uniform in x and y
nx (int) – Number of nodes in x
ny (int) – Number of nodes in y
shear (float) – Shear to apply in x direction
method (string) – name of generation method. Options are “spectral”, “Gaussian”, or “box”
pickle_file (string) – Name of pickled simFrac object. If a value is provided. The object will be loaded from file.
- Return type:
None
Notes
If nx and ny are provided, the resulted hx and hy must be the same.
- __init__(lx=None, ly=None, h=None, nx=None, ny=None, shear=None, method=None, units=None, pickle_file=None)[source]
Instanication of the SimFrac Object
- Parameters:
self (simFrac Object) –
units (string) – SI units for domain size, e.g., mm
lx (float) – Length of domain in x direction
ly (float) – Length of domain in x direction
h (float) – Dicretization length of domain. Uniform in x and y
nx (int) – Number of nodes in x
ny (int) – Number of nodes in y
shear (float) – Shear to apply in x direction
method (string) – name of generation method. Options are “spectral”, “Gaussian”, or “box”
pickle_file (string) – Name of pickled simFrac object. If a value is provided. The object will be loaded from file.
- Return type:
None
Notes
If nx and ny are provided, the resulted hx and hy must be the same.
- __weakref__
list of weak references to the object (if defined)
- apply_shear(shear=None)
Shifts the top surface along the x direction a distance of shear. Units of shear are in self.units.
- Parameters:
self (object) – simFrac Class
shear (float) – Value of shear in the x direction (Units are self.units)
- Return type:
None
Notes
Needs to be called for voxelization
- check_box_parameters()
Check that all required parameters for Gaussian field generation are provided. Exits if not.
- Parameters:
object (simfrac) –
- Return type:
None
Notes
None
- check_gaussian_parameters()
Check that all required parameters for Gaussian field generation are provided. Exits if not.
- Parameters:
object (simfrac) –
- Return type:
None
Notes
None
- check_generation_parameter(name, min_val=None, max_val=None)
Check parameter dictionary that the required key exists and has an acceptable value.
- Parameters:
name (str) – Name of the parameter
min_val (float) – Minimum accpetable value of the parameter
max_val (float) – Maximum accpetable value of the parameter
- Return type:
None
Notes
- check_spectral_parameters()
Check that all required parameters for spectral field generation are provided. Exits if not.
- Parameters:
object (simfrac) –
- Return type:
None
Notes
None
- combine_fractures(fracture_list, weights=None)
Combines multiple fracture surfaces using a point wise weighted linear superposition. Each point on the new fracture surface is the weighted summation of the points in the provided surfaces.
- Parameters:
fracture_list (list) – List of simfrac objects
weights (list) – List of floats for weighting in superposition. The length must match that of fracture_list
- Returns:
combined_fracture_list
- Return type:
simfrac object
Notes
All entries of fracture_list (simfrac objects) must have the same size and dimension.
If the weights are not normalizes, sum to 1, then the are normalized in proporiton.
If no weights are provided, the weights are set to be equal
- compute_acf(surface='all', num_lags=None)
Compute the correlation length of a field, both in x and y direction.
- Parameters:
self (object) – simFrac Class
surface (str) – Named of desired surface to plot. Options are ‘aperture’, ‘top’, ‘bottom’, and ‘all’(default).
num_lag (int) – Maximum number of lags. If no value is provided, num_lags is set to 1/4 the domain size in that direction.
- Return type:
None
Notes
Autocorrelation functions and first crossing estimates of correlation lengths are attached to the simfrac object.
- compute_moments()
Compute the moments of the distribution to screen
- Parameters:
self (object) – simFrac Class
- Return type:
None
Notes
None
- compute_variogram(surface='all', num_samples=500, max_lag=None, num_lags=10, model='spherical')
Compute the variogram of the surface using scikit-gstat.
- Parameters:
self (object) – simFrac Class
surface (str) – Name of desired surface acf to plot. Options are ‘aperture’, ‘top’, ‘bottom’, or ‘all’. Default value is ‘all’
num_samples (int) – Number of random samples used to compute the variogram
max_lag (int) – Maximum lag distance (unitless length).
num_lags (int) – Number of lag bins. Default is 10
model (str) – See https://scikit-gstat.readthedocs.io for model details. Default is spherical
- Return type:
None
Notes
scikit-gstat variogram object is attached to the simFrac object.
Reference: Mirko Mälicke, Egil Möller, Helge David Schneider, & Sebastian Müller. (2021, May 28).
mmaelicke/scikit-gstat: A scipy flavoured geostatistical variogram analysis toolbox (Version v0.6.0). Zenodo. http://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4835779
- create_box()
Box Kernel for convolution
- Parameters:
object (simfrac) –
- Return type:
None
Notes
For theoretical details see “Hyman, Jeffrey D., and C. Larrabee Winter. “Stochastic generation of explicit pore structures by thresholding Gaussian random fields.” Journal of Computational Physics 277 (2014): 16-31.”
- create_fracture()
Prints the generation methods parameters to screen
- Parameters:
self (simfrac object) –
- Return type:
None
Notes
Currently supported methods are “Guassian” and “Combined”
- create_gaussian()
Main generator of random fields following method described by Zinn and Harvey, 2003.
- Parameters:
object (simfrac) –
- Return type:
None
Notes
None
- create_spectral()
Generate a fracture surface using the spectral method.
- Parameters:
self (simfrac object) –
- Return type:
None
Notes
This method initializes the spectral method parameters, checks the parameters for consistency, and generates a fracture surface using the spectral method.
- dump_ascii(surface='all', filename_prefix=None, coordinates=False, indices=False)
Writes a surface fields to ascii files.
- Parameters:
self (object) – simFrac Class
surface (str) – Named of desired surface to write to file. Options are ‘aperture’, ‘top’, ‘bottom’, and ‘all’(default).
filename_prefix (str) – Prefix for filename
coordinates (bool) – True / False to write x/y coordinates to file
indices (bool) – True / False to write i/j indices to file
- Return type:
None
Notes
Files written out are aperture.dat, top.dat, and bottom.dat
- dump_surface_ascii(field, filename, coordinates, indices)
Writes a single field to ascii file.
- Parameters:
self (object) – simFrac Class
field (2D Numpy array) – Array of surface values
filename_prefix (str) – Prefix for filename
coordinates (bool) – True / False to write x/y coordinates to file
indices (bool) – True / False to write i/j indices to file
- Return type:
None
Notes
None
- from_pickle(filename)
Loads the simfrac object from a pickle format
- Parameters:
self (simfrac Object) –
filename (string) – name of pickle DFN object
- Return type:
simfrac object
Notes
- get_effective_aperture(model)
Estimate the effective aperture of the fractures.
- Models:
numerical : Estimates the effective aperture of the fracture by solving the Darcy flow equations using a Laplace equation for pressure in 2-dimensions.
gmean : Geometric average
hmean : Harmonic average
mean : Arthimatic average (amean, mean, average, arthimatic)
- Parameters:
model (string) – Currently available models: numerical, gmean, hmean, amean
- Return type:
None
Notes
Adds value to the effective_aperture dictionary on the simfrac class.
self.effective_aperture[‘<model>’]
- get_surface_cdf(surface)
create emperical CDF of surface of the fracture
- Parameters:
surface (string) – which surface of the fracture, Acceptable surfaces are ‘top’, ‘bottom’, ‘aperture’.
- Returns:
x (array) – x values of the cdf
cdf (array) – y valyes of the cdf
- get_surface_pdf(surface, num_bins, spacing='linear', x=None, weights=None, a_low=None, a_high=None, bin_edge='center')
create probability density function of a surface
- Parameters:
surface (string) – Select the surface of the fracture, Acceptable surfaces are ‘top’, ‘bottom’, ‘aperture’.
num_bins (int) – Number of bins in the pdf
spacing (string) – spacing for the pdf, options are linear and log, default is linear binning.
x (array) – array of bin edges
weights (array) – weights corresponding to vals to be used to create a weighted pdf
a_low (float) – lower value of bin range. If no value provided 0.95*min(vals) is used
a_high (float) – upper value of bin range. If no value is provided max(vals) is used
bin_edge (string) – which bin edge is returned. options are left, center, and right
- Returns:
bx (array) – bin edges or centers (x values of the pdf)
pdf (array) – values of the pdf, normalized so the Riemann sum(pdf*dx) = 1.
- gmean_effective_aperture()
Estimates the effective aperture of the fracture using the geometric mean
- Parameters:
None –
- Return type:
None
Notes
Adds value to the effective_aperture dictionary on the simfrac class.
self.effective_aperture[‘gmean’]
- hmean_effective_aperture()
Estimates the effective aperture of the fracture using the harmonic mean
- Parameters:
None –
- Return type:
None
Notes
Adds value to the effective_aperture dictionary on the simfrac class.
self.effective_aperture[‘hmean’]
- initialize_box_parameters()
Initializes parameters used in method box for fracture surface generation
- Parameters:
Object (simFrac) –
- Return type:
None
Notes
Attaches dictionary with parameters onto the simfrac object
- initialize_gaussian_parameters()
Initializes parameters used in method gaussian for fracture surface generation
- Parameters:
Object (simFrac) –
- Return type:
None
Notes
Attaches dictionary with parameters onto the simfrac object
- initialize_method()
Initializes defaults for a generation method
- Parameters:
self (simfrac object) –
- Return type:
None
Notes
Currently supported methods are “Guassian” an “Combined”
- initialize_parameters()
Initializes defaults for a generation method
- Parameters:
self (simfrac object) –
- Return type:
None
Notes
Currently supported methods are “Guassian” and “Combined”
- initialize_spectral_parameters()
Initializes parameters used in method spectral for fracture surface generation
- Parameters:
object (simFrac) –
- Return type:
None
Notes
Attaches dictionary with parameters onto the simfrac object
For theoretical details see: “Brown, Simple mathematical model of a rough fracture, J. of Geophysical Research, 100 (1995): 5941-5952” “Glover et al., Synthetic rough fractures in rocks, J. of Geophysical Research, 103 (1998): 9609-9620” “Glover et al., Fluid flow in synthetic rough fractures and application to the Hachimantai geothermal hot dry rock test site, 103 (1998): 9621-9635”
- legal()
Print the legal LANL statement for pySimFrac.
- Parameters:
self (object) – SurFrac Object
- Return type:
None
Notes
None
- mean_effective_aperture()
Estimates the effective aperture of the fracture using the arthimatic mean
- Parameters:
None –
- Return type:
None
Notes
Adds value to the effective_aperture dictionary on the simfrac class.
self.effective_aperture[‘mean’]
- numerical_effective_aperture()
Estimates the effective aperture of the fracture by solving the Darcy flow equations using a Laplace equation for pressure in 2-dimensions. The projected 2D aperture field is converted to permeability field using the local cubic law.
k = b^2 /12
Then the pressure field is obtained using second order finite difference scheme for the Laplace equation.
nabla cdot (k (bar{x}) nabla p) = 0
The Darcy velocity is obtained using this solution
q = -k/mu grad p
Then, Darcy’s law is inverted to obtain the effective permeability
keff = -(q mu)/grad p
and the effective aperture is
beff = sqrt(12*keff)
- Parameters:
self (simfrac object) –
- Return type:
None
Notes
mu drops out and we don’t actualy use it for numerical stability.
- pad(target_size)
- Parameters:
target_size (TYPE) – DESCRIPTION.
- Raises:
ValueError – DESCRIPTION.
- Return type:
None.
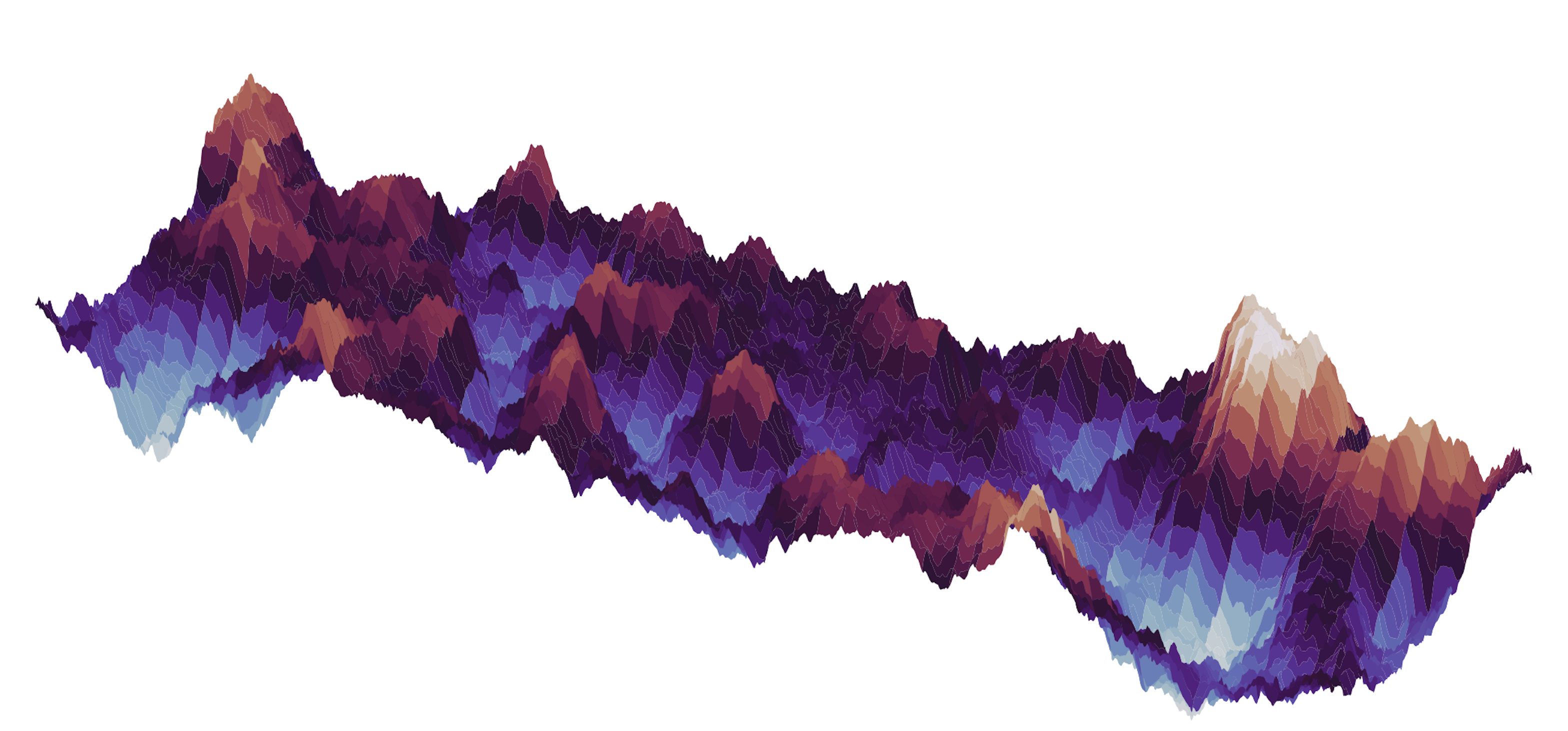
- plot_3D(edist=True)
- Parameters:
edist (booleam) – DESCRIPTION. The default is True.
- Return type:
None
- plot_acf(surface='all', figname=None)
Creates a plot of the autocorrelation function for surfaces.
- Parameters:
self (object) – simFrac Class
surface (str) – Name of desired surface acf to plot. Options are ‘aperture’, ‘top’, ‘bottom’, or ‘all’. Default value is ‘all’
figname (str) – Name of figure to be saved. If figname is None (default), then no figure is saved.
- Returns:
fig (Figure)
ax (Axes)
Notes
The autocorrelation functions will be computed if they have not be computed already.
- plot_aperture_field(figname=None)
Create a contour plot of the aperture field
- Parameters:
self (object) – simFrac Class
figname (str) – Name of figure to be saved. If figname is None (default), then no figure is saved.
- Returns:
fig (Figure)
ax (Axes)
Notes
None
- plot_surface(surface='both', figname=None)
Create a 3D surface plot
- Parameters:
self (object) – simFrac Class
surface (str) – Named of desired surface to plot. Options are ‘top’, ‘bottom’, and ‘both’(default).
figname (str) – Name of figure to be saved. If figname is None (default), then no figure is saved.
- Return type:
None
Notes
If surface name ‘aperture’ is provided, then plot_aperture_field is called.
- plot_surface_pdf(surface='all', bins='auto', figname=None)
Plots the probability density function of the fracture surface / aperture
- Parameters:
surface (string) – which surface of the fracture, Acceptable surfaces are ‘top’, ‘bottom’, ‘aperture’, or ‘all’.
bins (str, number, vector, or a pair of such values) – Generic bin parameter that can be the name of a reference rule, the number of bins, or the breaks of the bins.
figname (str) – Name of figure to save. If None, so figure is saved.
- Return type:
None
Notes
Uses Seaborn displot
- plot_variogram(surface='all', figname=None, show_lags=False)
Creates a plot of the autocorrelation function for surfaces.
- Parameters:
self (object) – simFrac Class
surface (str) – Name of desired surface acf to plot. Options are ‘aperture’, ‘top’, ‘bottom’, or ‘all’. Default value is ‘all’
figname (str) – Name of figure to be saved. If figname is None (default), then no figure is saved.
show_lags (bool) – True / False plot variogram as a function of Lag (unitless) or Lag Distance (units of grid resolution)
- Return type:
None
Notes
None
- print_method_params()
Prints the generation methods parameters to screen
- Parameters:
self (simfrac object) –
- Return type:
None
Notes
Different generation methods have different parameters used in their generation
- print_moments()
Print the moments of the distribution to screen
- Parameters:
self (object) – simFrac Class
- Return type:
None
Notes
None
- project_to_aperture()
Project the top and bottom surfaces onto a 2D aperture field.
- Parameters:
self (simfrac object) –
- Return type:
None
Notes
If bottom value is higher than top, set aperture on those nodes equal to 0.
- rescale_surface(method='mean')
- Parameters:
aperture (TYPE) – DESCRIPTION.
method (TYPE, optional) – DESCRIPTION. The default is ‘mean’.
- Return type:
None.
- reset_bottom()
Sets the minimum value of the bottom surface to 0
- Parameters:
self (object) – simFrac Class
- Return type:
None
Notes
Needs to be called for voxelization
- set_mean_aperture(mean_aperture=None)
Sets the mean aperture of the surface to the value mean_aperture
- Parameters:
self (object) – simFrac Class
mean_aperture (float) – Desired mean aperture value
- Return type:
None
Notes
None
- single_field_variogram(surface, num_samples, max_lag, num_lags, model)
Compute the variogram of a single field using scikit-gstat
- Parameters:
self (object) – simFrac Class
surface (str) – Name of desired surface acf to plot. Options are ‘aperture’, ‘top’, or ‘bottom’
num_samples (int) – Number of random samples used to compute the variogram
max_lag (int) – Maximum lag distance (unitless length).
num_lags (int) – Number of lag bins. Default is 10
model (str) – See https://scikit-gstat.readthedocs.io for model details. Default is spherical
- Return type:
None
Notes
scikit-gstat variogram object is attached to the simFrac object.
Requesting more than 10,000 samples can take a while.
- to_pickle(pickle_filename)
Saves the DFN object into a pickle format
- Parameters:
Object (SimFrac) –
pickle_filename (string) – Name of file.
- Return type:
None
Notes
None
- voxelize(solid_voxels=5)
- Parameters:
solid_voxels (TYPE, optional) – DESCRIPTION. The default is 5.
- Return type:
None.