GeoStatical analysis¶
Computing geostatistical information can be measured on fracture surfaces and projected aperture.
Variogram¶
We compute the empirical semivariogram for a surface as
The variogram is computed using the skgstat module. Please see that module for detailed documenation.
- pysimfrac.src.analysis.geostats_variogram.compute_variogram(self, surface='all', num_samples=500, max_lag=None, num_lags=10, model='spherical')[source]
Compute the variogram of the surface using scikit-gstat.
- Parameters:
self (object) – simFrac Class
surface (str) – Name of desired surface acf to plot. Options are ‘aperture’, ‘top’, ‘bottom’, or ‘all’. Default value is ‘all’
num_samples (int) – Number of random samples used to compute the variogram
max_lag (int) – Maximum lag distance (unitless length).
num_lags (int) – Number of lag bins. Default is 10
model (str) – See https://scikit-gstat.readthedocs.io for model details. Default is spherical
- Return type:
None
Notes
scikit-gstat variogram object is attached to the simFrac object.
Reference: Mirko Mälicke, Egil Möller, Helge David Schneider, & Sebastian Müller. (2021, May 28).
mmaelicke/scikit-gstat: A scipy flavoured geostatistical variogram analysis toolbox (Version v0.6.0). Zenodo. http://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4835779
- pysimfrac.src.analysis.geostats_variogram.single_field_variogram(self, surface, num_samples, max_lag, num_lags, model)[source]
Compute the variogram of a single field using scikit-gstat
- Parameters:
self (object) – simFrac Class
surface (str) – Name of desired surface acf to plot. Options are ‘aperture’, ‘top’, or ‘bottom’
num_samples (int) – Number of random samples used to compute the variogram
max_lag (int) – Maximum lag distance (unitless length).
num_lags (int) – Number of lag bins. Default is 10
model (str) – See https://scikit-gstat.readthedocs.io for model details. Default is spherical
- Return type:
None
Notes
scikit-gstat variogram object is attached to the simFrac object.
Requesting more than 10,000 samples can take a while.
To plot the emperical semi-variogram along with model, use plot_variogram described below
- pysimfrac.src.analysis.geostats_variogram.plot_variogram(self, surface='all', figname=None, show_lags=False)[source]¶
Creates a plot of the autocorrelation function for surfaces.
- Parameters:
self (object) – simFrac Class
surface (str) – Name of desired surface acf to plot. Options are ‘aperture’, ‘top’, ‘bottom’, or ‘all’. Default value is ‘all’
figname (str) – Name of figure to be saved. If figname is None (default), then no figure is saved.
show_lags (bool) – True / False plot variogram as a function of Lag (unitless) or Lag Distance (units of grid resolution)
- Return type:
None
Notes
None
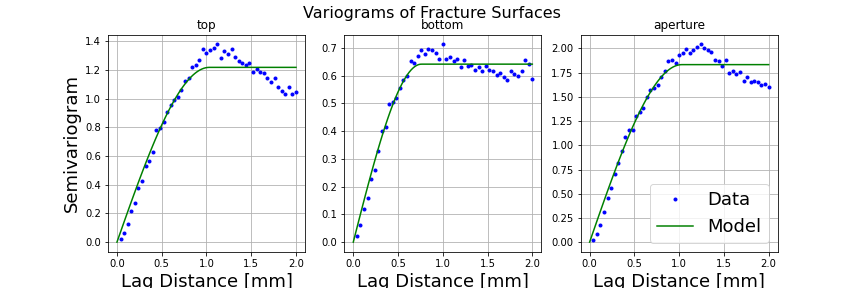
Variogram of a surface generated using the spectral method¶
Autocorrelation Function¶
We can computer the emperical auto correlation function in x and y directions on each surface. The correlation length in those direcitons is estimated using the first zero crossing of the autocorrelation funciton.
- pysimfrac.src.analysis.geostats_acf.compute_acf(self, surface='all', num_lags=None)[source]¶
Compute the correlation length of a field, both in x and y direction.
- Parameters:
self (object) – simFrac Class
surface (str) – Named of desired surface to plot. Options are ‘aperture’, ‘top’, ‘bottom’, and ‘all’(default).
num_lag (int) – Maximum number of lags. If no value is provided, num_lags is set to 1/4 the domain size in that direction.
- Return type:
None
Notes
Autocorrelation functions and first crossing estimates of correlation lengths are attached to the simfrac object.
- pysimfrac.src.analysis.geostats_acf.plot_acf(self, surface='all', figname=None)[source]
Creates a plot of the autocorrelation function for surfaces.
- Parameters:
self (object) – simFrac Class
surface (str) – Name of desired surface acf to plot. Options are ‘aperture’, ‘top’, ‘bottom’, or ‘all’. Default value is ‘all’
figname (str) – Name of figure to be saved. If figname is None (default), then no figure is saved.
- Returns:
fig (Figure)
ax (Axes)
Notes
The autocorrelation functions will be computed if they have not be computed already.
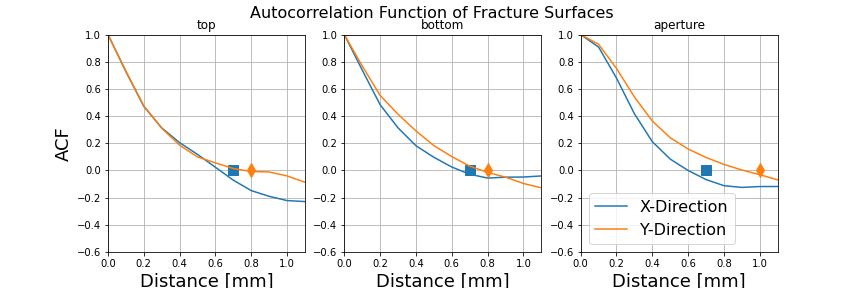
Autocorrelation functions of a surface generated using the spectral method¶
Probability Density Function¶
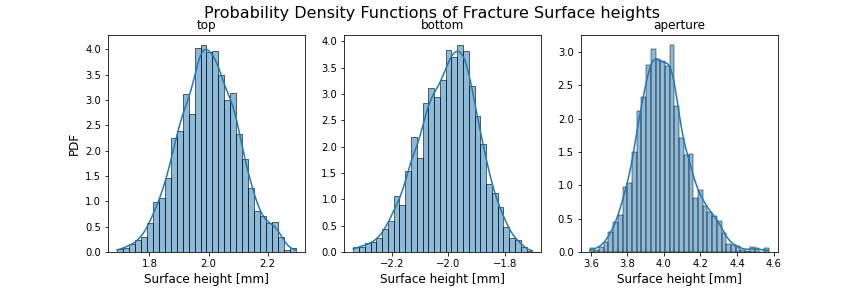
The empirical probability density of the surfaces can be directly observed.
PDFs¶
- pysimfrac.src.analysis.geostats.get_surface_pdf(self, surface, num_bins, spacing='linear', x=None, weights=None, a_low=None, a_high=None, bin_edge='center')[source]¶
create probability density function of a surface
- Parameters:
surface (string) – Select the surface of the fracture, Acceptable surfaces are ‘top’, ‘bottom’, ‘aperture’.
num_bins (int) – Number of bins in the pdf
spacing (string) – spacing for the pdf, options are linear and log, default is linear binning.
x (array) – array of bin edges
weights (array) – weights corresponding to vals to be used to create a weighted pdf
a_low (float) – lower value of bin range. If no value provided 0.95*min(vals) is used
a_high (float) – upper value of bin range. If no value is provided max(vals) is used
bin_edge (string) – which bin edge is returned. options are left, center, and right
- Returns:
bx (array) – bin edges or centers (x values of the pdf)
pdf (array) – values of the pdf, normalized so the Riemann sum(pdf*dx) = 1.
Below is an example of the PDF plot
Moments¶
The first four moments of the surface distributions can be directly computed.
- pysimfrac.src.analysis.geostats.compute_moments(self)[source]
Compute the moments of the distribution to screen
- Parameters:
self (object) – simFrac Class
- Return type:
None
Notes
None
- pysimfrac.src.analysis.geostats.print_moments(self)[source]
Print the moments of the distribution to screen
- Parameters:
self (object) – simFrac Class
- Return type:
None
Notes
None